Principles of Modern Chemistry 8th Edition Answers sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. This comprehensive guide delves into the fundamental principles of chemistry, providing a thorough understanding of the subject and empowering students with the knowledge they need to excel in their studies.
Through a series of engaging chapters, Principles of Modern Chemistry 8th Edition Answers explores the intricacies of atomic theory, the periodic table, chemical bonding, thermodynamics, chemical kinetics, and equilibrium. It delves into the properties of solutions, acids, bases, and pH, as well as the fascinating world of redox reactions and electrochemistry.
The book concludes with an in-depth examination of organic chemistry and biochemistry, providing a holistic understanding of the chemical world.
1. Understanding the Fundamental Principles

Modern chemistry is founded on the principles of atomic theory, which explains the structure and behavior of matter. The periodic table organizes elements based on their atomic properties, revealing trends and patterns that govern their chemical behavior.
Atomic Theory
- Atoms are the fundamental building blocks of matter, composed of a nucleus surrounded by electrons.
- The nucleus contains protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral).
- Electrons are negatively charged and orbit the nucleus in specific energy levels.
Periodic Table
- Organizes elements by increasing atomic number (number of protons).
- Groups (vertical columns) represent elements with similar chemical properties due to similar electron configurations.
- Periods (horizontal rows) represent elements with the same number of energy levels.
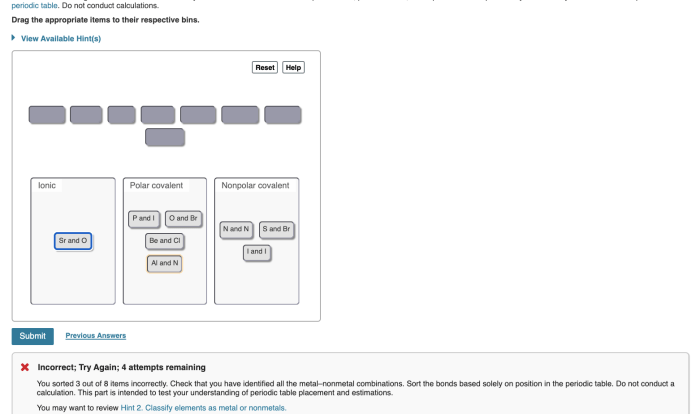
Chemical Bonding
- Chemical bonding occurs when atoms interact to form stable structures.
- Types of chemical bonds include ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds.
- Ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons between atoms, forming charged ions.
- Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms, forming molecules.
- Metallic bonds involve the delocalization of electrons in a metal lattice, giving metals their characteristic properties.
2. Thermodynamics and Chemical Reactions
Thermodynamics studies the flow of energy and its relationship to chemical reactions. The laws of thermodynamics provide a framework for understanding the spontaneity and equilibrium of chemical processes.
Laws of Thermodynamics
- First Law:Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred or transformed.
- Second Law:The entropy (disorder) of an isolated system always increases over time.
Thermodynamic Concepts
- Enthalpy:Heat released or absorbed during a chemical reaction at constant pressure.
- Entropy:Measure of the disorder or randomness of a system.
- Free Energy:The maximum amount of work that can be done by a system at constant temperature and pressure.
Chemical Reactions, Principles of modern chemistry 8th edition answers
- Spontaneity:A reaction that occurs without external input of energy.
- Equilibrium:A state in which the forward and reverse reactions occur at the same rate, resulting in no net change.
3. Chemical Kinetics and Equilibrium

Chemical kinetics studies the rates of chemical reactions and the factors that influence them. Chemical equilibrium describes the balance between the forward and reverse reactions in a chemical process.
Factors Affecting Reaction Rates
- Concentration of reactants
- Temperature
- Surface area of reactants
- Presence of a catalyst
Chemical Equilibrium
- A dynamic state where the forward and reverse reactions occur at equal rates.
- The equilibrium constant (Keq) is a measure of the relative amounts of reactants and products at equilibrium.
- Le Chatelier’s principle predicts how equilibrium will shift in response to changes in conditions.
Studying Reaction Rates
- Initial rate method:Measuring the initial rate of a reaction before significant changes occur.
- Integrated rate laws:Mathematical equations that describe the change in concentration of reactants or products over time.
- Rate-determining step:The slowest step in a multi-step reaction that determines the overall rate.
4. Solutions and Their Properties

Solutions are homogeneous mixtures of two or more substances. They exhibit unique properties that depend on the concentration and nature of the solutes and solvents.
Types of Solutions
- Solute:Substance that is dissolved in a solvent.
- Solvent:Substance that dissolves the solute.
- Concentrated solution:Contains a high concentration of solute.
- Dilute solution:Contains a low concentration of solute.
Concentration
- Molarity (M):Moles of solute per liter of solution.
- Molality (m):Moles of solute per kilogram of solvent.
- Percent by mass (% m/m):Mass of solute per 100 grams of solution.
Colligative Properties
- Vapor pressure lowering:Vapor pressure of a solution is lower than that of the pure solvent.
- Boiling point elevation:Boiling point of a solution is higher than that of the pure solvent.
- Freezing point depression:Freezing point of a solution is lower than that of the pure solvent.
General Inquiries: Principles Of Modern Chemistry 8th Edition Answers
What is the significance of atomic theory in modern chemistry?
Atomic theory provides the foundation for understanding the structure and behavior of matter. It explains that all matter is composed of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms, which have specific properties and can combine in various ways to form molecules and compounds.
How is the periodic table organized, and what trends can be observed?
The periodic table is organized based on the atomic number of elements, which increases from left to right and top to bottom. It exhibits periodic trends in properties such as atomic radius, ionization energy, and electronegativity, which can be used to predict the behavior and reactivity of elements.
What are the different types of chemical bonds, and how do they affect the properties of compounds?
There are three main types of chemical bonds: covalent, ionic, and metallic. Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms, ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons from one atom to another, and metallic bonds involve the sharing of electrons in a sea of delocalized electrons.
The type of bond formed affects the physical and chemical properties of the compound.