Price discrimination in airline industry – Price discrimination in the airline industry has emerged as a prevalent practice, sparking significant interest and debate. This comprehensive analysis delves into the multifaceted aspects of price discrimination, exploring its methods, market segmentation, revenue management, legal and ethical implications, impact on consumers, competitive dynamics, and future trends.
The intricate web of pricing strategies employed by airlines has profound implications for both consumers and the industry as a whole. Understanding the complexities of price discrimination is essential for navigating the ever-evolving landscape of air travel.
Price Discrimination in the Airline Industry: Price Discrimination In Airline Industry
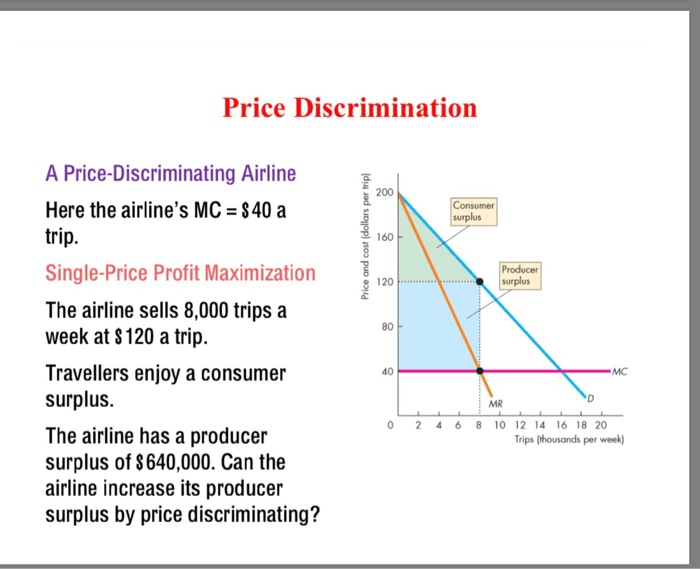
Price discrimination is a pricing strategy that involves charging different prices to different customers for the same or similar products or services. In the airline industry, price discrimination is used to maximize revenue and optimize capacity utilization. This article explores the various methods, market segmentation, revenue management, legal and ethical implications, impact on consumers, competitive dynamics, and future trends of price discrimination in the airline industry.
Price Discrimination Methods
Airlines use various price discrimination methods to segment their customers and charge different prices based on their willingness to pay. Some common methods include:
- Yield Management:Airlines adjust prices based on demand and availability, charging higher prices during peak travel times and lower prices during off-peak seasons.
- Advance Purchase Discounts:Airlines offer discounts to customers who purchase tickets well in advance, encouraging early bookings and reducing uncertainty.
- Group Discounts:Airlines offer discounted rates to groups of travelers, incentivizing larger bookings and filling empty seats.
- Loyalty Programs:Airlines reward frequent flyers with points, miles, and other perks, encouraging customer loyalty and repeat business.
- Personalized Pricing:Airlines use data analytics to tailor prices based on individual customer preferences and behavior, offering targeted discounts and promotions.
Each method affects consumer behavior differently. Yield management encourages flexibility and planning, while advance purchase discounts promote early booking. Group discounts incentivize group travel, and loyalty programs foster customer retention. Personalized pricing allows airlines to capture higher prices from value-conscious customers.
Advantages of price discrimination for airlines include increased revenue, improved capacity utilization, and targeted marketing. However, disadvantages include potential customer dissatisfaction, regulatory scrutiny, and ethical concerns.
Market Segmentation
Airlines target different market segments for price discrimination based on their travel patterns, preferences, and willingness to pay. Key market segments include:
- Business Travelers:Business travelers are typically price-insensitive and prioritize convenience and flexibility, making them a target for higher fares.
- Leisure Travelers:Leisure travelers are more price-sensitive and often seek value and flexibility, making them a target for discounts and promotions.
- Frequent Flyers:Frequent flyers are loyal customers who accumulate points and miles, making them a target for loyalty programs and personalized pricing.
- Group Travelers:Group travelers are typically price-sensitive and seek discounts for larger bookings, making them a target for group discounts.
- Value-Conscious Travelers:Value-conscious travelers are highly price-sensitive and seek the lowest possible fares, making them a target for personalized pricing and advance purchase discounts.
Airlines tailor their pricing strategies to each segment, offering targeted discounts, promotions, and loyalty programs to attract and retain customers.
Revenue Management
Revenue management is a critical aspect of price discrimination in the airline industry. Airlines use sophisticated algorithms to forecast demand, optimize pricing, and maximize revenue. Factors considered in revenue management decisions include:
- Demand Patterns:Airlines analyze historical and real-time data to predict demand for different flights and adjust prices accordingly.
- Competition:Airlines monitor competitor pricing and adjust their own prices to remain competitive and attract customers.
- Capacity Constraints:Airlines consider the number of seats available on each flight and adjust prices to fill empty seats and optimize capacity utilization.
- Cost Structure:Airlines consider their operating costs, including fuel, labor, and maintenance, to determine the minimum price they can charge.
Revenue management enables airlines to fine-tune their pricing strategies, increase revenue, and reduce empty seats.
Legal and Ethical Implications, Price discrimination in airline industry
Price discrimination in the airline industry is subject to legal and ethical considerations. Regulations and guidelines governing price discrimination include:
- Antitrust Laws:Antitrust laws prohibit airlines from engaging in predatory pricing or colluding to fix prices, ensuring fair competition.
- Consumer Protection Laws:Consumer protection laws prohibit airlines from engaging in deceptive or unfair pricing practices, ensuring transparency and fairness.
- Ethical Considerations:Ethical concerns related to price discrimination include potential unfairness to low-income travelers and the exploitation of consumers.
Airlines must carefully navigate these legal and ethical considerations to avoid regulatory penalties and maintain a positive public image.
Helpful Answers
What are the primary methods of price discrimination used by airlines?
Airlines commonly employ yield management, segmented pricing, and loyalty programs to implement price discrimination.
How does price discrimination affect consumer choice?
Price discrimination influences consumer choice by altering the perceived value and affordability of air travel. It can lead to increased demand from price-sensitive consumers and reduced demand from price-insensitive consumers.
What are the potential benefits of price discrimination for airlines?
Price discrimination allows airlines to maximize revenue by capturing different segments of the market and optimizing capacity utilization.

