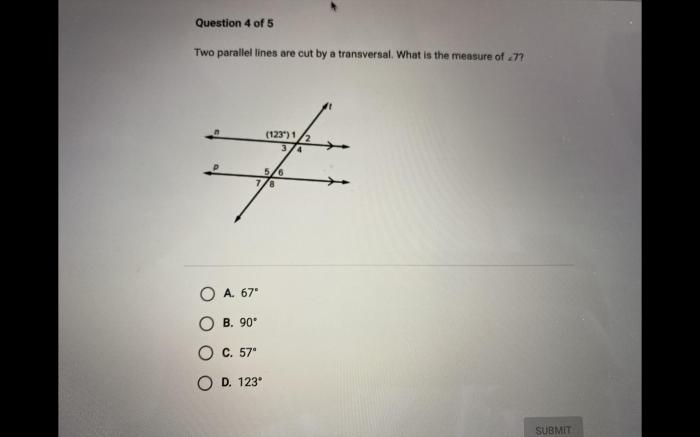
Two parallel lines cut by a transversal worksheet – Embark on an enlightening journey into the realm of geometry with our comprehensive worksheet on two parallel lines cut by a transversal. This engaging resource provides a thorough exploration of the fundamental concepts, properties, and applications of parallel lines, empowering you to unravel the intricacies of geometric intersections.
Delve into the captivating world of parallel lines, where transversals play a pivotal role in revealing hidden relationships. Discover the fascinating properties of alternate interior angles, alternate exterior angles, and corresponding angles, and witness how these properties serve as valuable tools for solving complex geometric problems.
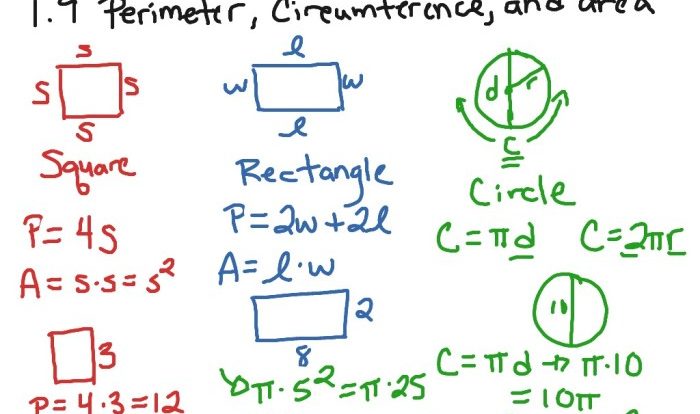
1. Geometric Definitions: Two Parallel Lines Cut By A Transversal Worksheet
In geometry, parallel lines are two lines that never intersect, no matter how far they are extended.
A transversal is a line that intersects two or more lines.
When a transversal intersects two parallel lines, it creates eight angles. These angles are named based on their position relative to the parallel lines and the transversal.
2. Properties of Intersecting Parallel Lines
When a transversal intersects two parallel lines, the following properties hold true:
- Alternate interior angles are congruent.
- Alternate exterior angles are congruent.
- Corresponding angles are congruent.
These properties can be used to solve geometric problems involving parallel lines.
3. Applications of Parallel Lines
Parallel lines have many practical applications in everyday life and various fields, including:
- Architecture: Parallel lines are used to create the walls, floors, and ceilings of buildings.
- Engineering: Parallel lines are used to design bridges, roads, and other structures.
- Design: Parallel lines are used to create patterns and designs in art, fashion, and other fields.
Understanding parallel lines can aid in spatial reasoning and problem-solving.
4. Proofs and Theorems Related to Parallel Lines
The Angle Sum Theorem states that the sum of the interior angles of a triangle is 180 degrees. This theorem can be used to prove that parallel lines never intersect.
The Parallel Postulate states that through a given point not on a given line, there is exactly one line that is parallel to the given line.
These theorems and proofs are essential for understanding the properties of parallel lines and their applications in geometry.
FAQ Corner
What is the definition of a transversal?
A transversal is a line that intersects two or more other lines at distinct points.
How can I identify alternate interior angles?
Alternate interior angles are non-adjacent angles that lie on opposite sides of the transversal and inside the parallel lines.
What is the relationship between corresponding angles?
Corresponding angles are angles that are located in the same position relative to the transversal and the parallel lines.