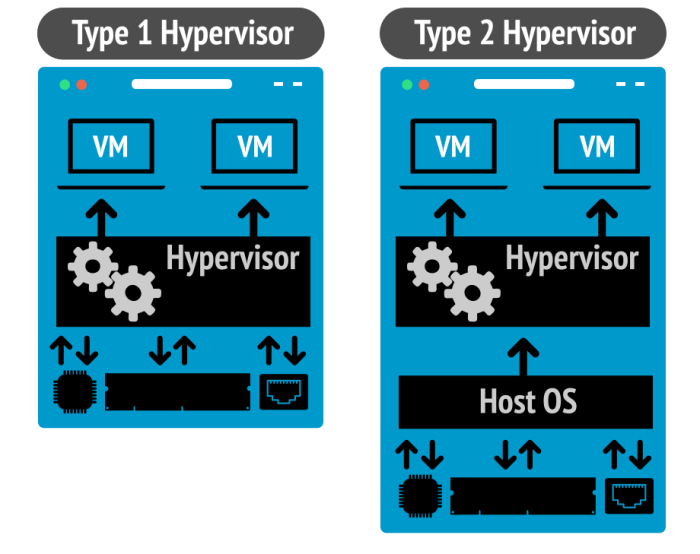
Type 2 hypervisors cannot be used on laptops – Type 2 hypervisors, despite their advantages, are inherently incompatible with laptops. This incompatibility stems from fundamental technical limitations that hinder their effective operation on portable devices.
Delving into the technicalities, Type 2 hypervisors rely on the host operating system, which introduces a performance overhead and resource contention. Additionally, their reliance on hardware virtualization extensions, which are often absent in laptops, further limits their viability.
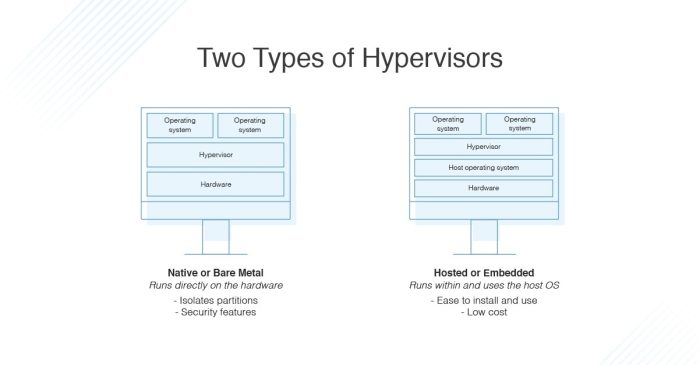
Overview of Type 2 Hypervisors: Type 2 Hypervisors Cannot Be Used On Laptops
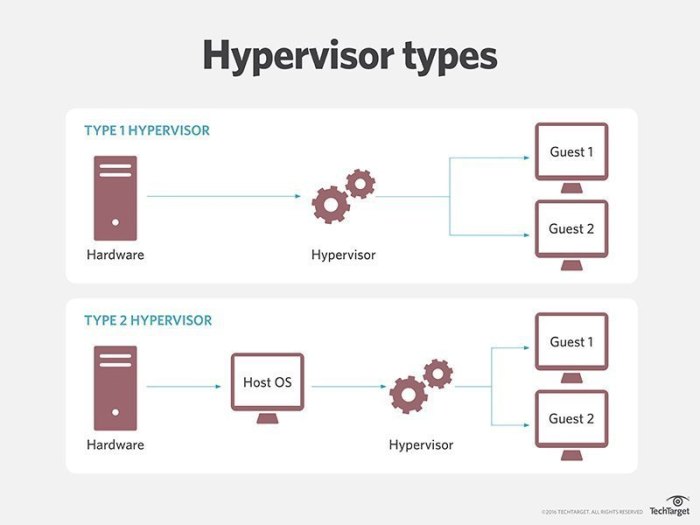
Type 2 hypervisors, also known as hosted hypervisors, operate as software applications within a host operating system. They provide a virtualized environment that runs on top of the host OS, allowing multiple guest operating systems to be executed simultaneously.
Unlike Type 1 hypervisors, which directly interact with hardware and manage physical resources, Type 2 hypervisors rely on the host OS for hardware access and resource allocation. This makes them less efficient and more resource-intensive compared to Type 1 hypervisors.
Limitations of Type 2 Hypervisors on Laptops, Type 2 hypervisors cannot be used on laptops
Type 2 hypervisors are not well-suited for laptops due to several limitations:
- Performance Overhead:Type 2 hypervisors introduce an additional layer of software between the hardware and the guest operating systems, resulting in performance degradation compared to Type 1 hypervisors.
- Resource Utilization:Type 2 hypervisors consume significant system resources, including memory and CPU cycles, which can impact the performance of the host operating system and guest workloads.
- Compatibility Issues:Type 2 hypervisors may not be compatible with all hardware devices, particularly those designed for low-power consumption, which are commonly found in laptops.
Alternative Virtualization Options for Laptops
For laptops, alternative virtualization solutions exist that offer better performance and compatibility:
- Containerization:Containerization involves isolating applications and their dependencies within lightweight, isolated containers that share the same kernel as the host operating system. It offers a more efficient and portable virtualization solution for laptops.
- Virtual Machine Platforms:Virtual machine platforms, such as VirtualBox and VMware Fusion, provide a more lightweight and resource-efficient alternative to Type 2 hypervisors. They offer better compatibility with hardware and can run multiple guest operating systems simultaneously.
Considerations for Virtualization on Laptops
When choosing a virtualization solution for laptops, several factors should be considered:
- Hardware Compatibility:Ensure that the virtualization solution is compatible with the laptop’s hardware, including the CPU, memory, and peripherals.
- Performance Requirements:Consider the performance overhead and resource utilization of the virtualization solution and its impact on the host operating system and guest workloads.
- Security Implications:Assess the security implications of running multiple guest operating systems on a laptop, including potential vulnerabilities and isolation mechanisms.
FAQ Section
Why can’t Type 2 hypervisors be used on laptops?
Type 2 hypervisors rely on the host operating system, which introduces performance overhead and resource contention. Additionally, they require hardware virtualization extensions, which are often absent in laptops.
What are the alternatives to Type 2 hypervisors for laptops?
Containerization and Type 1 hypervisors are viable alternatives to Type 2 hypervisors for laptops. Containerization provides lightweight virtualization, while Type 1 hypervisors offer better performance and isolation.