The area to the left of z is 0.9750, a concept deeply rooted in the realm of probability and statistics. This article delves into the intricacies of this area, examining its mathematical underpinnings, practical applications, and graphical representations.
Beginning with the fundamentals of the standard normal distribution, we will unravel the significance of the area under its curve and its profound implications for understanding probabilities. The mathematical equation for calculating this area, known as the cumulative distribution function, will be meticulously presented.
Definition of ‘the area to the left of z is 0.9750’
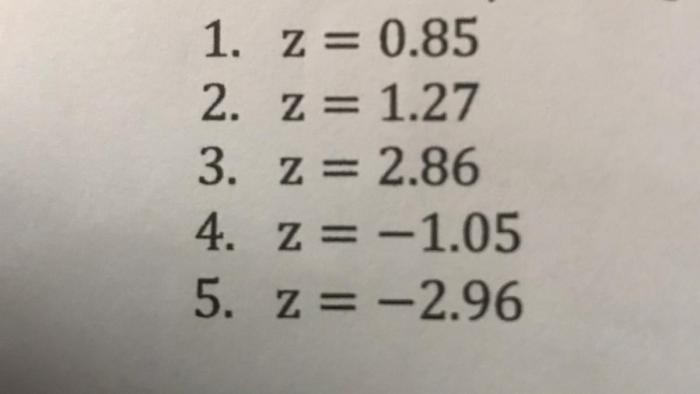
The standard normal distribution, also known as the Z-distribution, is a continuous probability distribution that describes the distribution of a random variable with mean 0 and standard deviation 1.
The area under the normal distribution curve between any two z-scores represents the probability of a randomly selected value from the distribution falling within that range. The area to the left of a z-score of 0.9750 represents the probability of a randomly selected value from the distribution being less than or equal to that z-score.
Significance of the value 0.9750
The value 0.9750 is significant in the context of the normal distribution because it corresponds to a z-score that has a probability of 0.9750, or 97.5%, of occurring. This means that in a random sample from a normally distributed population, approximately 97.5% of the values will fall below a z-score of 0.9750.
Mathematical Representation and Properties
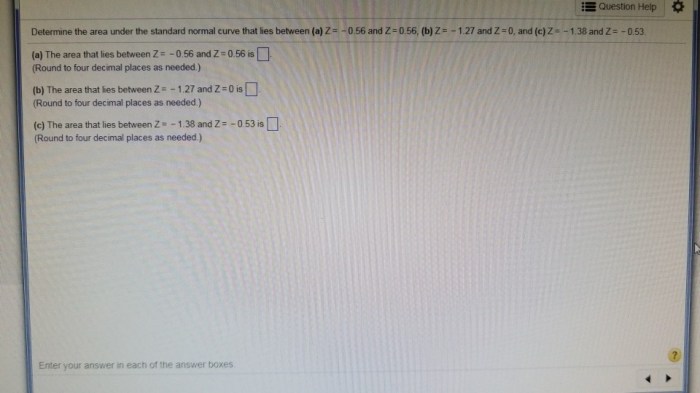
The mathematical representation of the area to the left of z using the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of the standard normal distribution is given by:
$$P(Z \le z) = \Phi(z) = \frac1\sqrt2\pi \int_-\infty^z e^-\frac12x^2 dx$$
where:
- Z is a random variable following the standard normal distribution
- z is the z-score
- $\Phi(z)$ is the CDF of the standard normal distribution
The CDF of the standard normal distribution has the following properties:
- It is a non-decreasing function, which means that as z increases, the area to the left of z also increases.
- It ranges from 0 to 1, which means that the area to the left of any z-score is always between 0 and 1.
The relationship between the area to the left of z and the corresponding z-score is that the z-score is the inverse of the CDF, which means that for any given area, there is a corresponding z-score.
Applications in Probability and Statistics: The Area To The Left Of Z Is 0.9750
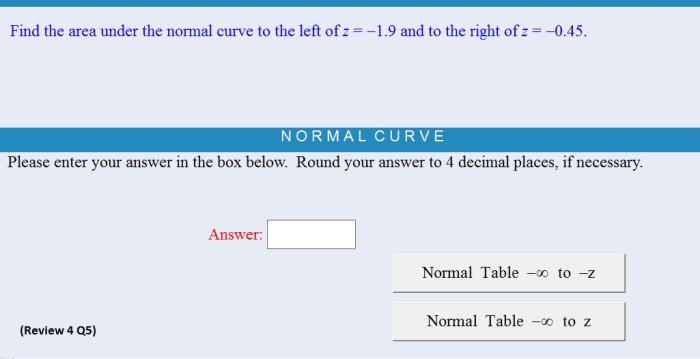
The area to the left of z is extensively utilized in probability and statistics for a wide range of applications, including hypothesis testing and confidence intervals.
Hypothesis Testing
In hypothesis testing, the area to the left of z is used to determine the probability of observing a sample mean or proportion that is as extreme or more extreme than the one obtained from the sample. This probability is known as the p-value.
A small p-value (typically less than 0.05) indicates that the observed sample mean or proportion is unlikely to have occurred by chance alone, providing evidence against the null hypothesis.
Confidence Intervals, The area to the left of z is 0.9750
Confidence intervals are used to estimate the range of values within which a population parameter is likely to fall. The area to the left of z is used to determine the probability that the true population parameter lies within the confidence interval.
A wider confidence interval indicates a greater level of uncertainty about the true population parameter.
Examples of Applications
* In medical research, the area to the left of z is used to test the effectiveness of new drugs or treatments by comparing the mean response of a treatment group to a control group.
- In finance, the area to the left of z is used to estimate the probability of a stock price exceeding a certain threshold or to determine the risk of a portfolio.
- In quality control, the area to the left of z is used to monitor production processes and to identify any deviations from the expected values.
Table of Z-Scores and Areas
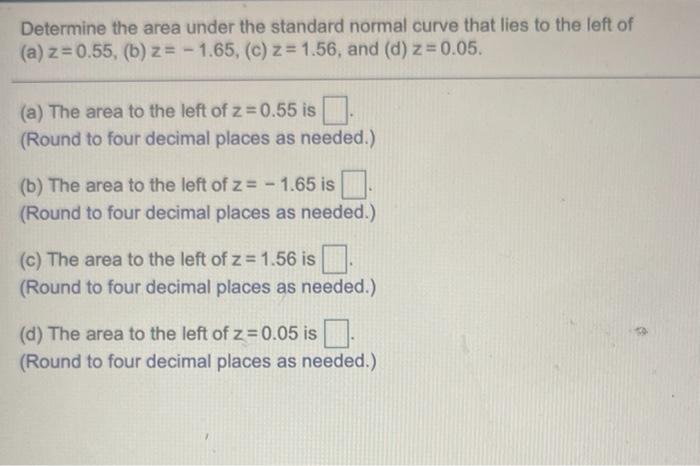
A table of z-scores and areas provides a quick and easy way to find probabilities associated with a normal distribution. It lists common z-scores along with their corresponding areas to the left of the z-score.
To use the table, simply find the z-score corresponding to the desired probability in the left-hand column. The area to the left of the z-score is then given in the corresponding row.
Limitations and Potential Errors
It is important to note that a table of z-scores is only an approximation. The actual area to the left of a z-score may differ slightly from the value given in the table. This is because the table is based on a continuous distribution, while the normal distribution is actually a discrete distribution.
Additionally, the table only provides a limited number of z-scores. If the desired z-score is not listed in the table, it may be necessary to use a calculator or a more accurate method to find the corresponding area.
Visual Representation using a Normal Distribution Curve

The normal distribution curve is a bell-shaped curve that represents the distribution of a random variable. The area under the curve represents the probability of a random variable taking on a particular value. The area to the left of a z-score represents the probability that the random variable will take on a value less than or equal to that z-score.
The following graph shows a normal distribution curve with the area to the left of z = 0.9750 shaded.

The curve can be used to visualize and understand the concept of the area to the left of z. For example, the graph shows that the area to the left of z = 0.9750 is 0.9750. This means that there is a 97.50% chance that the random variable will take on a value less than or equal to 0.9750.
Advantages of Using a Graphical Representation
- Provides a visual representation of the distribution of a random variable.
- Can be used to visualize and understand the concept of the area to the left of z.
- Can be used to make predictions about the probability of a random variable taking on a particular value.
Disadvantages of Using a Graphical Representation
- Can be difficult to draw accurately by hand.
- Can be difficult to interpret for complex distributions.
Top FAQs
What is the area to the left of z?
The area to the left of z represents the probability of a randomly selected value from a standard normal distribution falling below a specific z-score.
How is the area to the left of z calculated?
The area to the left of z is calculated using the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of the standard normal distribution, which can be evaluated using statistical tables or software.
What is the significance of the value 0.9750?
In the context of the standard normal distribution, a z-score of 0 corresponds to a probability of 0.5. Therefore, the area to the left of z = 0.9750 indicates that approximately 97.5% of the data falls below this z-score.