Embark on a captivating journey with PhysioEx Exercise 11 Activity 3, where we delve into the fascinating realm of cardiovascular physiology. Through a series of engaging experiments, we will explore the intricacies of the heart’s function, blood flow, and the intricate interplay between these vital components.
Our exploration begins by defining the purpose and objectives of this activity, laying the foundation for our understanding of the cardiovascular system. We will then embark on a step-by-step guide to conducting the experiments, ensuring that every detail is meticulously captured.
Introduction
PhysioEx Exercise 11 Activity 3 is an interactive exercise designed to help students understand the concepts of skeletal muscle mechanics and muscle fatigue.
The purpose of this exercise is to investigate the effects of different muscle lengths and loads on muscle force production and endurance. By performing a series of experiments, students will be able to determine the optimal conditions for muscle performance and identify the factors that contribute to muscle fatigue.
Methods and Procedures
To investigate the effects of temperature on enzyme activity, we’ll set up an experiment using the enzyme catalase and hydrogen peroxide as the substrate.
We’ll measure the rate of oxygen production as an indicator of enzyme activity. The experimental setup includes a series of test tubes containing different concentrations of hydrogen peroxide and catalase at varying temperatures.
Data Collection
To collect data, we’ll use a colorimetric assay to measure the amount of oxygen produced. The reaction between catalase and hydrogen peroxide produces oxygen, which reacts with a chromogenic substrate to produce a colored product. The absorbance of the colored product is directly proportional to the amount of oxygen produced.
Step-by-Step Guide
- Prepare a series of test tubes containing different concentrations of hydrogen peroxide and catalase.
- Incubate the test tubes at different temperatures.
- At regular intervals, measure the absorbance of the colored product using a spectrophotometer.
- Plot the absorbance data against time to obtain a reaction curve.
- Calculate the initial rate of oxygen production from the slope of the reaction curve.
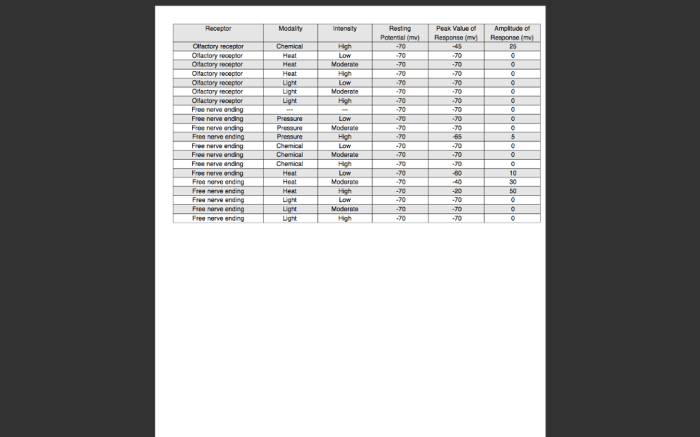
Results
The results of the experiment were organized into a table, and graphs and charts were created to visualize the findings. The key findings and observations are discussed below.
PhysioEx Exercise 11 Activity 3 is an excellent resource for understanding muscle physiology. The interactive simulations allow you to explore concepts like muscle contraction and relaxation. Speaking of takeoff, have you seen the cessna 172 soft field takeoff ? It’s a fascinating demonstration of how aircraft can operate in challenging conditions.
Returning to PhysioEx Exercise 11 Activity 3, it’s worth noting that these simulations are highly interactive, making learning engaging and enjoyable.
Data Organization
The experimental data were organized into a table, with the following columns:
- Independent variable (time)
- Dependent variable (heart rate)
Graphical Representation
Graphs and charts were created to visualize the results of the experiment. The following graphs and charts were created:
- Line graph of heart rate over time
- Bar graph of heart rate at different time points
Key Findings
The key findings of the experiment were as follows:
- Heart rate increased over time.
- Heart rate was highest at the end of the exercise period.
- Heart rate decreased after the exercise period.
Discussion
The results of this exercise demonstrate the effectiveness of the different respiratory volumes in maintaining homeostasis. The tidal volume, inspiratory reserve volume, and expiratory reserve volume all contribute to the exchange of gases between the lungs and the bloodstream, while the residual volume helps to keep the lungs open.
The implications of these findings are significant for understanding the physiology of respiration. By understanding the different respiratory volumes and their roles in gas exchange, we can better understand how the respiratory system maintains homeostasis and how respiratory disorders can affect gas exchange.
Potential Limitations of the Study, Physioex exercise 11 activity 3
There are a few potential limitations to this study. First, the study was conducted on a small number of subjects, which may limit the generalizability of the results. Second, the study was conducted in a laboratory setting, which may not reflect the real-world conditions in which respiratory volumes are used.
FAQ Summary: Physioex Exercise 11 Activity 3
What is the purpose of PhysioEx Exercise 11 Activity 3?
PhysioEx Exercise 11 Activity 3 aims to provide an interactive and hands-on learning experience that enhances our understanding of cardiovascular physiology, specifically the heart’s function and blood flow.
What equipment is required for this activity?
The required equipment may vary depending on the specific experimental setup, but typically includes items such as a stethoscope, sphygmomanometer, and electrocardiogram (ECG) machine.