Prepare to unravel the mysteries of immunity with our exclusive Immunity Pogil Answer Key PDF. Embark on a journey where complex immunological concepts are demystified, empowering you with a comprehensive understanding of this fascinating biological system.
Delve into the intricacies of innate and adaptive immunity, deciphering the roles of various immune cells and their intricate interplay in safeguarding your body against invading pathogens.
Definition and Overview of Immunity

Immunity refers to the body’s ability to protect itself from foreign invaders, such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites. It consists of two main types: innate immunity and adaptive immunity.
Innate immunity is the body’s first line of defense, which provides immediate but non-specific protection against pathogens. It includes physical barriers like the skin and mucous membranes, as well as chemical barriers like stomach acid and antimicrobial peptides.
Adaptive immunity, on the other hand, is more specific and develops over time. It involves the production of antibodies and the activation of specialized immune cells, such as T cells and B cells, which target and eliminate specific pathogens.
Types of Immune Cells
- Neutrophils:Phagocytic cells that engulf and destroy pathogens.
- Macrophages:Larger phagocytic cells that also present antigens to other immune cells.
- Dendritic cells:Specialized cells that capture and present antigens to T cells.
- T cells:Cells that recognize and destroy infected cells.
- B cells:Cells that produce antibodies against specific pathogens.
The Immune Response
The immune response is a complex process involving the activation and coordination of various immune cells. When a pathogen enters the body, innate immune cells recognize it and trigger an inflammatory response, which attracts other immune cells to the site of infection.
Adaptive immune cells then become activated and specific to the pathogen. They proliferate and differentiate into effector cells, which directly attack and eliminate the pathogen. Memory cells are also produced, which provide long-term immunity against future infections by the same pathogen.
Acquired Immunity and Vaccination
Innate immunity, the first line of defense, provides immediate protection against pathogens, but it is not specific to particular pathogens. Acquired immunity, on the other hand, is highly specific and develops over time as the body encounters specific pathogens.
Acquired immunity involves the production of antibodies, proteins that recognize and neutralize specific pathogens. This process is mediated by lymphocytes, white blood cells that differentiate into B cells and T cells.
Vaccines
Vaccines are biological preparations that induce acquired immunity without causing the disease itself. They contain weakened or inactivated forms of pathogens or their antigens, which stimulate the immune system to produce antibodies and memory cells.
Types of Vaccines
- Live-attenuated vaccines:Contain weakened but live pathogens that can replicate in the body, stimulating a strong immune response.
- Inactivated vaccines:Contain killed pathogens that cannot replicate but still retain their antigens, inducing antibody production.
- Toxoid vaccines:Contain inactivated toxins produced by bacteria, stimulating antibody production against the toxin rather than the pathogen itself.
- Subunit vaccines:Contain purified antigens from pathogens, inducing antibody production against specific proteins.
- mRNA vaccines:Contain messenger RNA (mRNA) that encodes specific antigens, which are then translated by the body’s cells, stimulating antibody production.
Cell-Mediated Immunity: Immunity Pogil Answer Key Pdf
Cell-mediated immunity (CMI) is a type of immune response that does not involve antibodies. Instead, it relies on the activation of T cells to directly attack and destroy infected cells or cancer cells.
CMI is essential for fighting intracellular pathogens, such as viruses and bacteria that live inside host cells. It also plays a role in the rejection of foreign tissues, such as in organ transplantation.
Role of T Cells in Cell-Mediated Immunity
T cells are a type of white blood cell that play a central role in CMI. There are two main types of T cells: cytotoxic T cells (Tc cells) and helper T cells (Th cells).
The immunity pogil answer key pdf is a great resource for students who are studying the immune system. It provides detailed explanations of the immune system and its functions. If you are interested in learning more about the immune system, I recommend checking out the ear nose and throat diagram . This diagram provides a detailed overview of the structures and functions of the ear, nose, and throat.
The immunity pogil answer key pdf is a great resource for students who are studying the immune system. It provides detailed explanations of the immune system and its functions.
Cytotoxic T cellsdirectly kill infected cells or cancer cells by releasing cytotoxic substances, such as perforin and granzymes. These substances create pores in the target cell’s membrane, causing the cell to lyse (break open).
Helper T cellsactivate other immune cells, such as cytotoxic T cells and macrophages. They also release cytokines, which are signaling molecules that help coordinate the immune response.
Different Types of T Cells and Their Functions
- Th1 cells: Help activate cytotoxic T cells and macrophages. They are important for fighting intracellular pathogens.
- Th2 cells: Help activate B cells, which produce antibodies. They are important for fighting extracellular pathogens.
- Th17 cells: Help activate neutrophils and macrophages. They are important for fighting extracellular bacteria and fungi.
- Regulatory T cells (Tregs): Suppress the immune response. They help prevent the immune system from attacking the body’s own tissues.
Antibody-Mediated Immunity
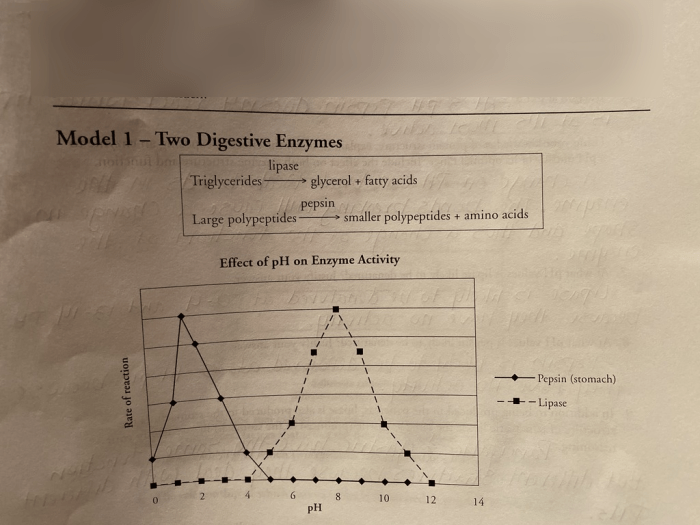
Antibody-mediated immunity (AMI), also known as humoral immunity, is a type of immune response that involves the production of antibodies by B cells. Unlike cell-mediated immunity, which targets infected cells directly, AMI focuses on neutralizing pathogens and toxins in body fluids.
Role of B Cells
B cells are white blood cells that play a crucial role in AMI. They produce antibodies, which are proteins that bind to specific antigens (foreign molecules) on the surface of pathogens. This binding neutralizes the pathogens, preventing them from infecting cells.
Types of Antibodies
There are five main classes of antibodies, each with its unique function:
IgM
The first antibody produced in response to an infection, it binds to multiple antigens and activates the complement system.
IgG
The most abundant antibody in the blood, it neutralizes toxins and viruses.
IgA
Found in saliva, tears, and breast milk, it protects mucosal surfaces from infection.
IgE
Involved in allergic reactions, it binds to allergens and triggers the release of histamine.
IgD
Found on the surface of B cells, it helps in antigen recognition and activation.
Immune System Disorders
The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to protect the body from infection and disease. However, sometimes the immune system can malfunction, leading to a variety of disorders.
Immune system disorders can be classified into two main types: autoimmune diseases and immunodeficiency disorders.
Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues. This can lead to a wide range of symptoms, depending on the specific organs or tissues that are affected.
- Causes:The exact cause of autoimmune diseases is unknown, but they are thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
- Symptoms:Symptoms of autoimmune diseases can vary widely, depending on the specific disease. However, some common symptoms include fatigue, pain, swelling, and inflammation.
- Treatment:There is no cure for autoimmune diseases, but treatment can help to manage the symptoms and prevent complications.
Immunodeficiency Disorders
Immunodeficiency disorders occur when the immune system is unable to function properly, making the body more susceptible to infection and disease.
- Causes:Immunodeficiency disorders can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetic defects, infections, and certain medications.
- Symptoms:Symptoms of immunodeficiency disorders can vary depending on the severity of the disorder. However, some common symptoms include frequent infections, fatigue, and weight loss.
- Treatment:Treatment for immunodeficiency disorders depends on the underlying cause. In some cases, treatment may involve antibiotics, antiviral medications, or immunoglobulin replacement therapy.
Immunological Techniques
Immunological techniques are indispensable tools for studying the complex mechanisms of the immune system. These techniques enable researchers and clinicians to analyze immune responses, identify and characterize immune cells, and diagnose and monitor immune disorders.
A wide range of immunological techniques have been developed, each with its unique principles and applications. Some of the most commonly used techniques include:
Flow Cytometry
Flow cytometry is a technique that allows for the analysis of individual cells based on their physical and chemical characteristics. Cells are stained with fluorescent antibodies specific to different cell surface markers or intracellular proteins. The stained cells are then passed through a flow cytometer, which measures the fluorescence intensity and other parameters for each cell.
Flow cytometry can be used to identify and quantify different cell populations, study cell activation and differentiation, and analyze immune responses.
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
ELISA is a technique used to measure the concentration of specific proteins in a sample. It involves coating a solid surface with an antigen or antibody specific to the target protein. The sample is then added to the surface, and any target protein present will bind to the immobilized antigen or antibody.
After washing away unbound material, an enzyme-linked antibody is added, which binds to the target protein. The enzyme substrate is then added, and the amount of colored product formed is proportional to the concentration of the target protein in the sample.
Immunohistochemistry, Immunity pogil answer key pdf
Immunohistochemistry is a technique used to localize and visualize specific proteins within cells or tissues. Tissue sections are stained with antibodies specific to the target protein, and the bound antibodies are visualized using a chromogenic or fluorescent substrate. Immunohistochemistry can be used to study the distribution and expression of proteins in different cell types and tissues, and to identify and characterize immune cells in situ.
Immunoprecipitation
Immunoprecipitation is a technique used to isolate and purify specific proteins from a complex mixture. It involves incubating the sample with an antibody specific to the target protein. The antibody-protein complexes are then precipitated out of solution using protein A or protein G beads.
Immunoprecipitation can be used to purify proteins for further analysis, such as mass spectrometry or Western blotting.
Western Blotting
Western blotting is a technique used to separate and identify specific proteins in a sample based on their molecular weight. Proteins are separated by electrophoresis on a polyacrylamide gel and then transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane. The membrane is incubated with an antibody specific to the target protein, and the bound antibody is visualized using a chromogenic or fluorescent substrate.
Western blotting can be used to confirm the presence of specific proteins, study protein expression levels, and identify post-translational modifications.
Top FAQs
What is the purpose of the Immunity Pogil Answer Key PDF?
The Immunity Pogil Answer Key PDF provides comprehensive solutions to the questions and exercises found in the Pogil activities on immunity, aiding students in their understanding of immunological concepts.
How can I access the Immunity Pogil Answer Key PDF?
The Immunity Pogil Answer Key PDF is available for download from reputable educational websites or online repositories. Ensure you obtain it from a trusted source to guarantee its accuracy and authenticity.